A Sunday on La Grande Jatte — 1884 1886
“Bedlam,” “scandal,” and “hilarity” were among the epithets used to describe what is now considered Georges Seurat’s greatest work, and one of the most remarkable paintings of the nineteenth century, when it was first exhibited in Paris. Seurat labored extensively over [i]A Sunday on La Grande Jatte—1884[/i], reworking the original as well as completing numerous preliminar...
- Size:
- 207.5 x 308.1 cm
- Medium:
- Oil on canvas
- Credit:
- Courtesy of the Art Institute of Chicago
More from this artist...
Loading...
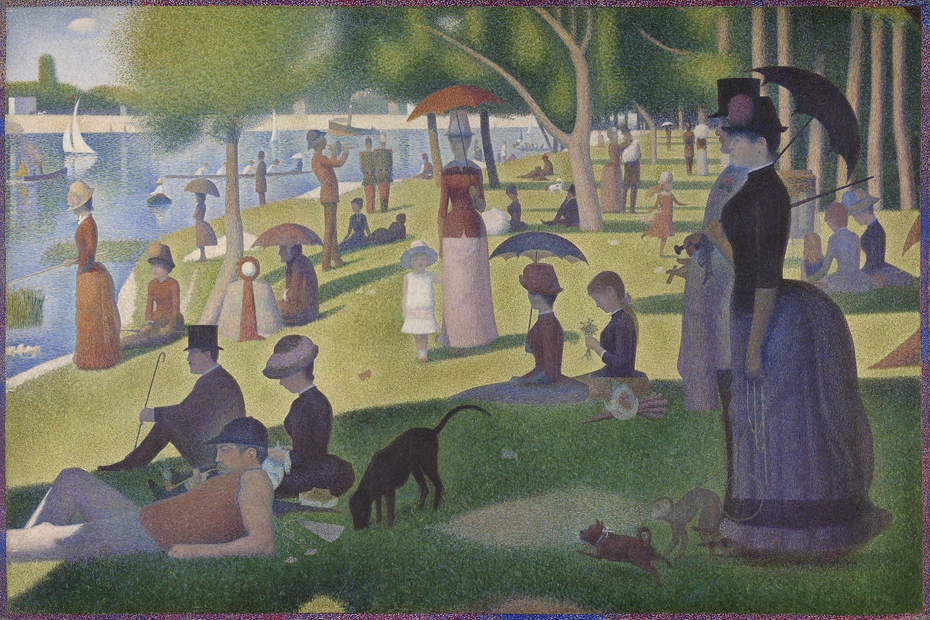














Discussion