Neoclassicism
"The one way for us to become great, perhaps inimitable, is by imitating the ancients."
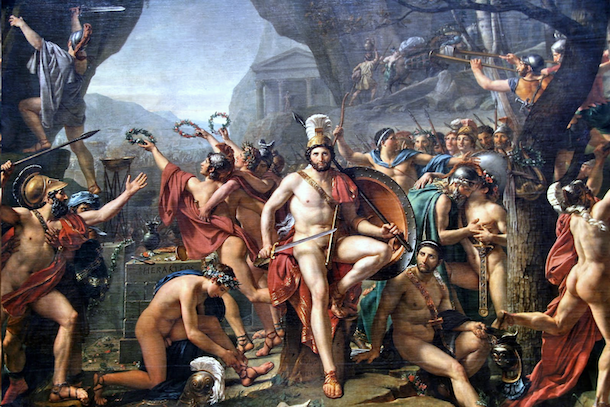
Neoclassicism is the 18th and 19th century movement that developed in Europe as a reaction to the excesses of Baroque and Rococo styles that were dominant in the previous era. The movement sought to return to the classical beauty and magnificence of the Ancient Greece and the Roman Empire. Neoclassical art is based on simplicity and symmetry and takes its inspiration from the German art historian Johann Joachim Winckelmann who believed that art should aim at the ideal forms and beauty of Greek art. Explore the Neoclassicism movement by starting from What is Neoclassicism? and browse our curated list of artworks from neoclassicism painters such as Jacques-Louis David, Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres and others.
What is Neoclassicism?
Neoclassicism is the 18th and 19th century movement that developed in Europe as a reaction to the excesses of Baroque and Rococo. The movement sought to return to the classical beauty and magnificence of the Ancient Greece and the Roman Empire. Neoclassical art is based on simplicity and symmetry and takes its inspiration from the German art historian Johann Joachim Winckelmann who believed that art should aim at the ideal forms and beauty of Greek art. As he wrote:
“The one way for us to become great, perhaps inimitable, is by imitating the ancients.”
The revival of artistic canons of classical antiquity came from the admiration for Renaissance art, as well as Enlightenment and the earlier classical painting of the French artist Nicolas Poussin, as well as from a dissatisfaction towards Rococo and towards the overwhelming Baroque style. Whereas Romantic artists sought to paint the cruelty and vitality of action, neoclassical painters wanted to depict the beauty and the harmony of a subject. They combine an idealistic style, using perspective with drama and forcefulness according to Winckelmann's definition of the movement as "noble simplicity and calm grandeur". Neoclassical works, therefore, are serious, unemotional and heroic. Restraint and simplicity, along with precise depiction and close congruence of clear form and noble content, are the main characteristics of Neoclassicism.
Neoclassicism was developed in Rome at first, but its popularity spread throughout Europe during the 18th century due to the Grand Tour; the trip in which European students travelled around the continent. At that moment the great collections of antiquities began to be discovered and re-evaluated and a neoclassical revival spread across Europe. Many European art students who had made the Grand Tour, in fact, returned to their country from Italy with the rediscovered Greek-Roman ideals. The neoclassical movement involved the decorative and visual arts, literature, theater, music and architecture and it continued to evolve until the early 19th century when it started to compete against the movement of Romanticism. Learn more about the movement in History of Neoclassicism.
Text by Cristina Motta